Server, Client, or Relay? Dual-Role Detection of Circumvention Relays
Authors: Sultan Almutairi (North Carolina State University), Khaled Harfoush (North Carolina State University), Yannis Viniotis (North Carolina State University)
Year: 2026
Issue: 1
Pages: 58–61
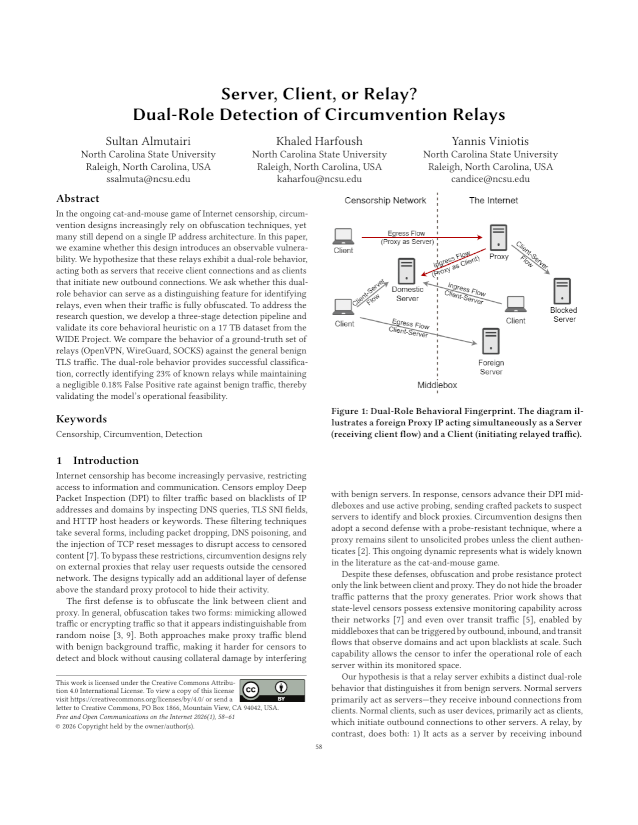
Abstract: In the ongoing cat-and-mouse game of Internet censorship, circumvention designs increasingly rely on obfuscation techniques, yet many still depend on a single IP address architecture. In this paper, we examine whether this design introduces an observable vulnerability. We hypothesize that these relays exhibit a dual-role behavior, acting both as servers that receive client connections and as clients that initiate new outbound connections. We ask whether this dual- role behavior can serve as a distinguishing feature for identifying relays, even when their traffic is fully obfuscated. To address the research question, we develop a three-stage detection pipeline and validate its core behavioral heuristic on a 17 TB dataset from the WIDE Project. We compare the behavior of a ground-truth set of relays (OpenVPN, WireGuard, SOCKS) against the general benign TLS traffic. The dual-role behavior provides successful classification, correctly identifying 23% of known relays while maintaining a negligible 0.18% False Positive rate against benign traffic, thereby validating the model’s operational feasibility.
Copyright in FOCI articles are held by their authors. This article is published under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 license.